# 2033. Minimum Operations to Make a Uni-Value Grid
Question link is here.
This is the second question of this week's weekly contest.
# Question
You are given a 2D integer grid of size m x n and an integer x. In one operation, you can add x to or subtract x from any element in the grid.
A uni-value grid is a grid where all the elements of it are equal.
Return the minimum number of operations to make the grid uni-value. If it is not possible, return -1.
Example 1:
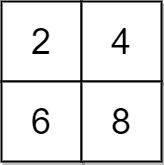
Input: grid = [[2,4],[6,8]], x = 2
Output: 4
Explanation: We can make every element equal to 4 by doing the following:
- Add x to 2 once.
- Subtract x from 6 once.
- Subtract x from 8 twice.
A total of 4 operations were used.
Example 2:
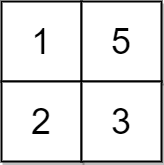
Input: grid = [[1,5],[2,3]], x = 1
Output: 5
Explanation: We can make every element equal to 3.
Example 3:
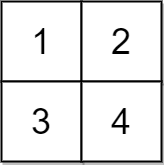
Input: grid = [[1,2],[3,4]], x = 2
Output: -1
Explanation: It is impossible to make every element equal.
# Solution
We can simply treat the grid as an array. It's obvious that the optimal value to want to reach is within the range of Max(Array) and Min(Array).
Therefore, our choice is to increase the smallest value or decrease the largest value. Each time we choose to increase/decrease the value with the smallest value count. I.E. if we have an array of 1,1,2,3,4. Than we will choose to decrease 4 instead of increase both 1. And each time we increase/decrease the value until it is the same with another value in the array or it exceed the min/max value in the array. In the latter case, we can make all value to become the same. And after each increase/decrease, we need to update value count for the corresponding value. I.E if we have 1,1,2,3,4,4 and we choose to increase 1. Before the increment, we have count(1) = 2, count(2) = 1, after the increment we have count(1) = 0, count(2) = 3. The counter is used to calculated the cost of the increase/decrease of each value.
class Solution:
def minOperations(self, grid: List[List[int]], x: int) -> int:
res = []
countOdd = 0
countEven = 0
dic = {}
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] % 2 == 0:
countEven += 1
else:
countOdd += 1
if x % 2 == 0 and countOdd != 0 and countEven != 0:
return -1
if(grid[i][j] not in dic.keys()):
res.append(grid[i][j])
dic[grid[i][j]] = dic.get(grid[i][j], 0) + 1
if(len(dic.keys()) == 1):
return 0
res.sort()
ans = 0
while True:
if dic[res[0]] <= dic[res[-1]]:
Min = res[0]
count = dic[Min]
dic[Min] = 0
while Min + x not in dic.keys():
ans += count
Min += x
if Min > res[-1]:
return -1
ans += count
dic[Min + x] = dic[Min + x] + count
res.pop(0)
if(len(res) == 1):
return ans
else:
Max = res[-1]
count = dic[Max]
dic[Max] = 0
while Max - x not in dic.keys():
ans += count
Max -= x
if Max < res[0]:
return -1
ans += count
dic[Max - x] += count
res.pop(-1)
if(len(res) == 1):
return ans
Time complexity: .